Reporters: Mr. Sujinda Saehan, Mr. Ekkajak Intarat, Mr. Nitigon Jumniansuk, Mr. Thanet Sangseejun
Evidence Date: April 1st, 2024
 Related SDGs:
Related SDGs:
Related Indicators: 6.3.1, 6.3.2, 6.5.1, 6.5.3, 6.5.4, 6.5.5, 6.5.7
Details:
On April 1, 2024, the Water Management Research Team from the Faculty of Engineering, Rajamangala University of Technology Srivijaya (RUTS), was invited by the executives, council president, and administrators of the Khlong Ree Subdistrict Administrative Organization in Sathing Phra District, Songkhla Province, to conduct a comprehensive assessment of salinity levels in Songkhla Lake. Recent observations have indicated that salinity levels in certain areas of the lake have risen above 2 parts per thousand (ppt), creating significant challenges for the Sathing Phra Peninsula. This increase in salinity is affecting the availability and quality of domestic water resources, agricultural activities, and aquaculture production, thereby posing both environmental and socio-economic risks to local communities.
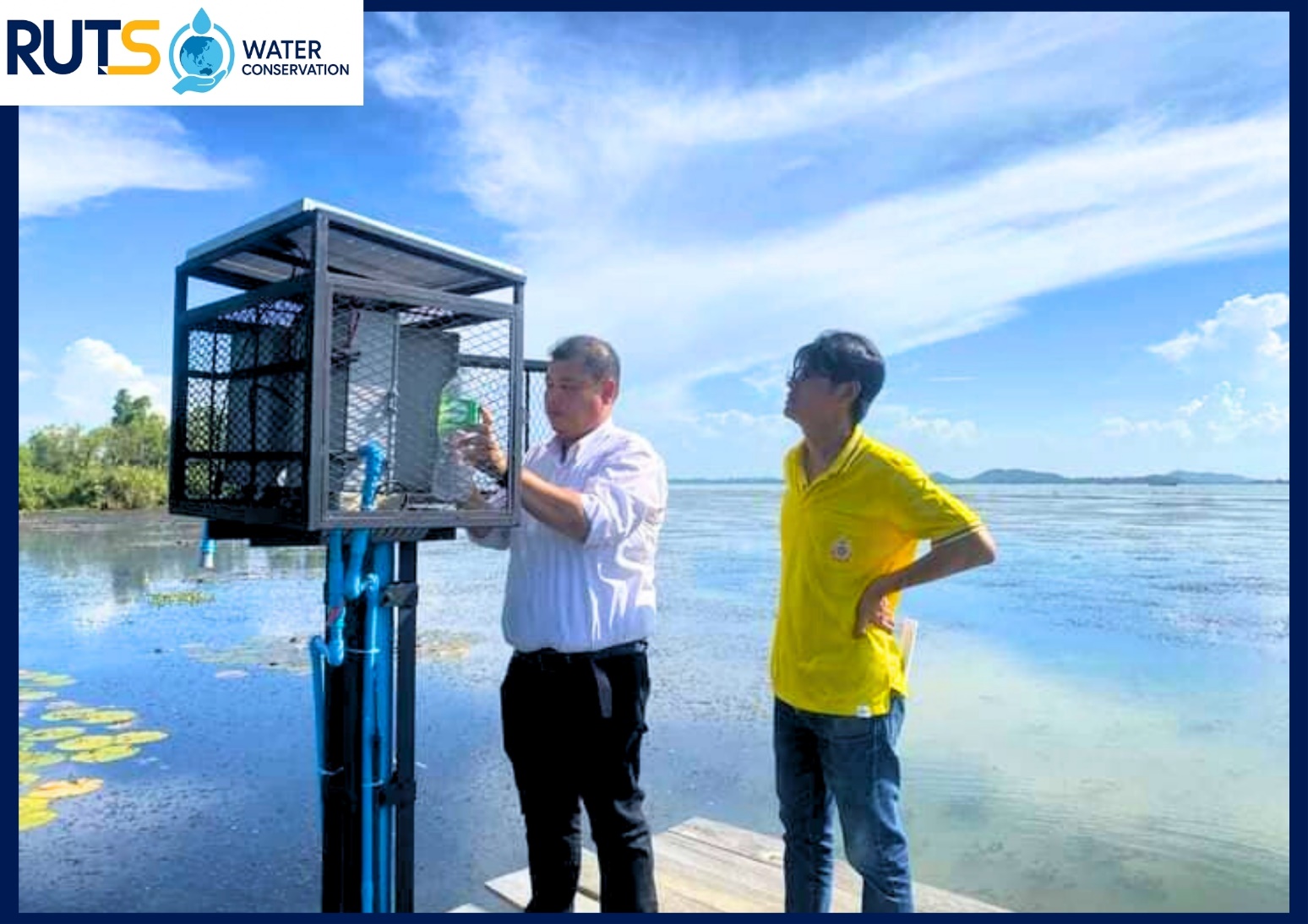
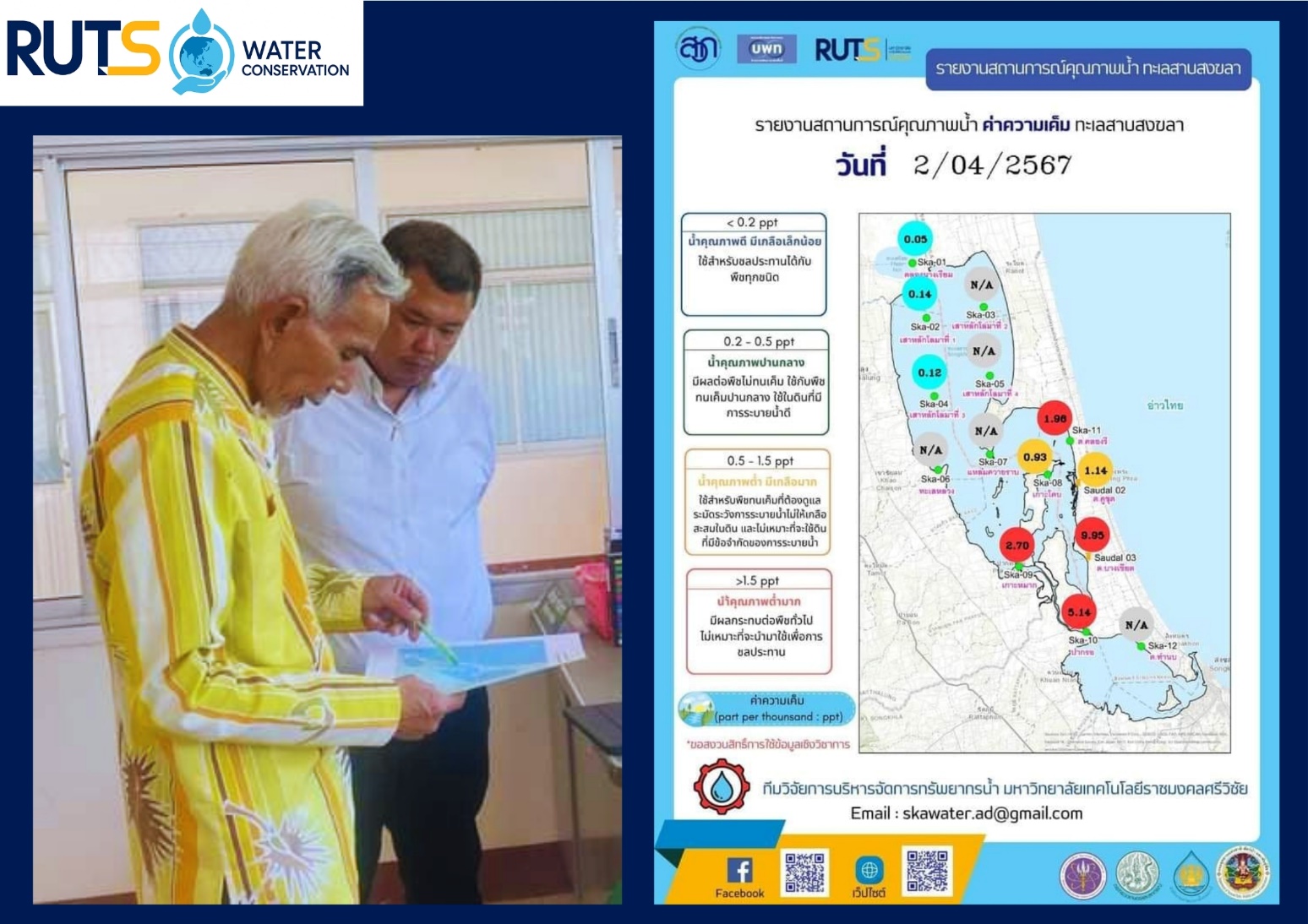

The assessment and monitoring efforts were carried out in close collaboration with multiple stakeholders, particularly local community innovators engaged under the project “Scaling Up Water Management Innovation for Rice and Shrimp Farmers in the Songkhla Lake Basin.” These community innovators are integral to the monitoring system, collecting and reporting real-time data on salinity levels. Their contributions ensure timely decision-making and effective management of water resources. Specific operational guidelines have been established based on salinity readings: when salinity is ≤ 1.5 ppt, water is pumped in for storage to support agricultural and domestic needs, while pumping operations are suspended if salinity exceeds 1.5 ppt, preventing harmful impacts on crop production and household water supply.
The data gathered by these monitoring efforts are also being used to inform the District Disaster Relief Committee in declaring and responding to water-related emergencies, highlighting the practical application of academic research in supporting community resilience and disaster preparedness. This integrated approach demonstrates the potential of combining scientific knowledge, local participation, and technology for sustainable water resource management and climate adaptation.

The project exemplifies a strong alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation), which aims to ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. By monitoring salinity and regulating water use, RUTS and its partners are contributing directly to improving water quality, safeguarding water accessibility for households, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. Moreover, the project addresses broader SDG 6 targets, including water efficiency, local water governance, and the resilience of communities to climate-induced water stress. Through this initiative, local communities not only gain access to reliable water resources but also acquire the skills and knowledge needed to respond to environmental changes, furthering the goal of building adaptive, water-secure societies.
Supported by the Program Management Unit for Competitiveness (PMUC) and RUTS, the project underscores the critical role of universities as local think tanks. Academic institutions are leveraging their research capacity to generate actionable insights, integrate technological solutions, and foster community participation in water management. By translating research into practical interventions, RUTS demonstrates how higher education institutions can lead in sustainable water resource management, facilitate climate adaptation, and contribute meaningfully to global sustainability agendas.
In conclusion, the monitoring and assessment of salinity in Songkhla Lake illustrate a successful model of community-engaged, data-driven water management, linking scientific research with local action. The collaboration between RUTS researchers, community innovators, and local authorities ensures that interventions are timely, effective, and aligned with SDG 6, fostering sustainable water resource management and strengthening community resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
Related Links:



